The Benefits of Composting and Mulching

Anúncios
Gardening is not only a fulfilling hobby, but also an opportunity to contribute to the natural world around you. Composting and mulching are two easy to implement but very effective gardening practices that every gardener should do. Familiarizing yourself with the benefits they offer will help you make informed decisions and take important steps toward environmentally responsible gardening.
1. What is composting?
Composting is the natural process by which organic material is recycled into nutrient-rich humus. Examples of compostable items include food scraps, yard waste, and plant matter. This dark granular powder can be used as a fertilizer as well as a soil improver.
Anúncios
2. Benefits Of Composting
Improve Soil Quality:
When you use compost, your soil benefits from the addition of important nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium. These nutrients are vital to plant development and the overall health of your garden, helping to promote robust and vibrant plant life.
Reduce the Amount of Waste in Landfills:
Composting organic waste can significantly reduce the amount of material sent to landfill. This reduces greenhouse gas production and reduces pressure on landfill capacity.
Anúncios
Reduce the Occurrence of Plant Diseases:
Compost contains beneficial bacteria that help suppress dangerous pathogens, reduce the risk of plant diseases and create a healthier garden. Compost also contains microorganisms that help improve soil fertility.
Improve Soil Structure:
Using compost can improve soil structure, especially clay or sandy soils. It improves the water retention capacity of sandy soils and increases the drainage capacity of clay soils, creating a favorable environment for plant roots to grow.
Attract Beneficial Organisms:
Earthworms and other beneficial organisms grow especially well in soil that contains a lot of compost. These organisms contribute to nutrient cycling, soil aeration and overall soil health.
Promote Ecological Gardening:
Composting is an important part of ecologically responsible gardening. If you return organic waste to the soil from which it came, you complete the cycle and reduce the use of fertilizer in your garden.
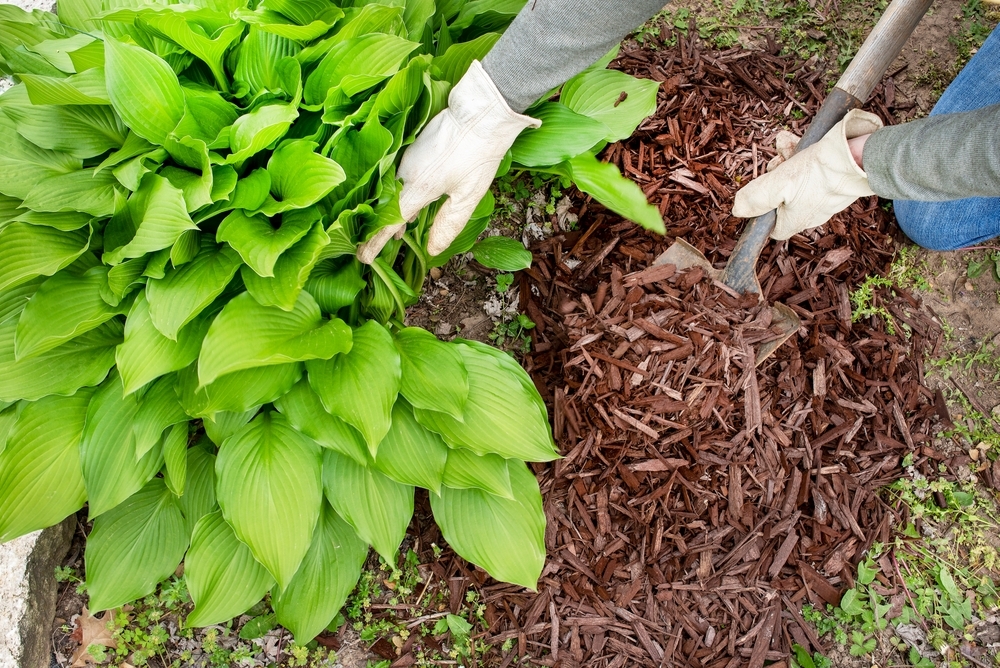
3. What Does Cover Include?
Covering the soil surface with a layer of organic or inorganic material such as leaves, straw, wood chips or gravel is called mulching. This layer of protection can be used for a variety of tasks and is of great value.
4. Some Benefits of Coverage
Stay Hydrated:
Mulch acts as a natural barrier, preventing water loss through evaporation from the top layers of the soil. This helps retain moisture, reducing watering time and saving water.
Control Weeds:
Weed growth can be prevented by applying a thick layer of mulch, which blocks sunlight and inhibits weed seed germination. This results in a reduced need for herbicides and weed control by humans.
Adjust Soil Temperature:
Thanks to the insulating effect of the mulch, the soil stays cool in the warmer months and warmer in colder weather. This helps to keep the soil temperature constant, which is good for the roots of the plant.
Preventing Soil Erosion:
Using mulch protects the soil from wind and rain, helping to maintain its structural integrity and integrity.
Improve Soil Fertility:
As organic mulch decomposes, the nutrients it contains are released into the soil, fertilizing the soil and helping the plants thrive.
To Improve the Appearance of the Garden:
Using mulch can bring order and tidiness to your yard. In addition, it has the potential to improve the overall look and feel of the landscape.
5. Mulch and Compost together Make a Winning Combination
Composting and mulching are great practices and complement each other. Compost can be used to create a nutrient-rich mulch and provide additional benefits to the soil and plants. These practices combine to create a garden ecology that is both resilient and thriving.
Conclusion:
Composting and mulching are two basic practices that are essential to promoting sustainable gardening and good for the environment. These practices contribute to a healthier, greener planet by improving plant health, conserving water and other resources, reducing waste and enriching the soil.
FAQs:
1. Can I only compost kitchen waste, or should garden waste also be included?
For best results, it is recommended to compost a mix of kitchen waste (fruit and vegetable scraps, coffee grounds) and yard waste (leaves, grass clippings, twigs).
2. How long does it take for compost to be usable?
The composting process usually takes several months to a year, depending on factors such as the composting method, materials used, and environmental conditions.
3. Can I use colored mulch in the garden?
Colored mulch is usually made from recycled wood waste and is safe to use. However, it is best to choose natural organic mulch to avoid possible chemical additives.
4. How often should I top up my yard with mulch?
Mulch breaks down over time, so it’s best to supplement it once or twice a year to maintain effectiveness.
5. Can I use compost as mulch for garden beds?
Yes, compost can be used as mulch in garden beds to enrich the soil and provide plants with additional nutrients.